Top 5 Industrial Chair Features for Aerospace Manufacturing in Singapore
In Singapore’s aerospace manufacturing sector, high-precision manufacturing plants require more than efficient labor and advanced equipment—more importantly, they require comfortable and reliable working furniture, especially seating. Wherever the operations are component assembly, inspection, or testing stations, the seat selection has direct impacts on the comfort, safety, and productivity of operators.
Rather than looking at specific chair manufacturers, this article examines the top five essentials an industrial chair needs to have to meet the unique requirements of aerospace manufacturing in Singapore.
Why Seating Matters in Aerospace Production
Aerospace production work—such as constructing turbines, wiring avionics, or testing composite components—is typically repetitive, intricate, and performed over long periods. Poor seating may lead to fatigue, musculoskeletal disease, and even lower production accuracy. Ergonomic seating isn’t an indulgence in comfort—it’s a requirement for efficiency and quality assurance in aerospace factories.
Singapore’s aerospace industry, led by global industry participants like Rolls-Royce, Pratt & Whitney, and ST Engineering, rests on credible standards, accuracy in work, and strict EHS (Environment, Health, Safety) compliance. Since plane maintenance, repair, and overhaul become increasingly required, optimizing the work environment—included in that the design of the chair—helps reach delivery schedules without negatively affecting employee health.
Top 5 Characteristics of Industrial Aerospace Application Chairs
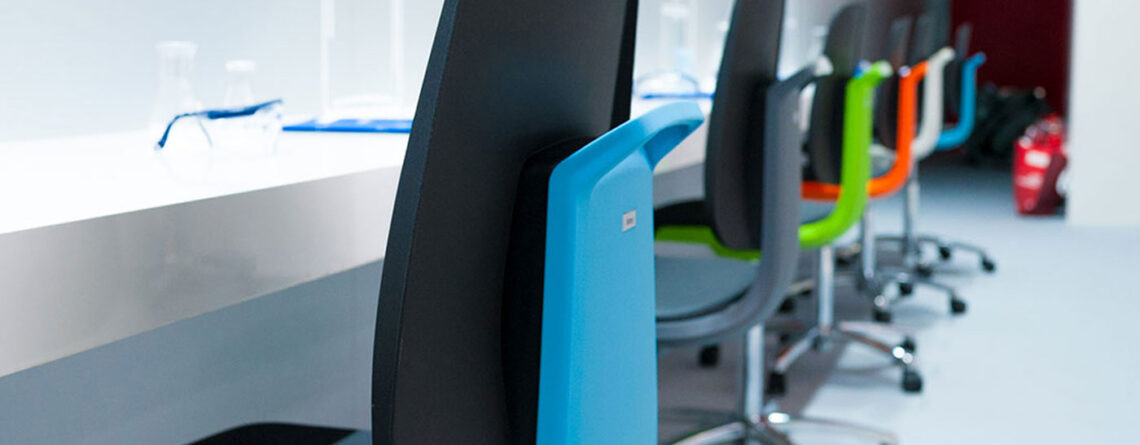
1. Ergonomic Adjustability
Industrial chairs should fit the body, rather than the reverse. Choose seats that are adjustable for:
- Varying levels of workstation
- Forward-leaning activities using tilt in the back to hold the spine firm
- Adjusting seat depth to pad out thighs without stifling blood supply
- Lower back strain support to reduce load
Technicians alternate between sitting and standing work, thus adjustable-setting chairs ensure all the users maintain a healthy posture based on body shape or work duty.
2. ESD Protection
Factory chairs must be designed to endure harsh usage. Aerospace production floors have a tendency to feature heavy-duty tooling, metal shards, and occasional oil or chemical spills. Chairs should be:
- Impact- and scratch-resistant
- Chemically resistant, especially against adhesives, oils, and cleaners
- Heavy usage resistant, with heavy-duty load-carrying frames and extended-wear surfaces
This resistance maintains low replacement cycles, making them a sound long-term investment—especially in heavy-use working zones like hangars or MRO lines.
3. Hard-Wearing Construction for High-Demand Areas
Static electricity is an unnoticed threat in avionics assembly environments. A single electrostatic discharge (ESD) is capable of annihilating sensitive electronic components in flight control or communications systems.
Industrial chairs used in aerospace production sites must have:
- Conductive castors or glides
- Seat and frame material of ESD-dissipative quality
- Grounding chains or points
These aspects incorporate the chair into the larger EPA (Electrostatic Protected Area) of the facility, accommodating teams with international standards of ESD protection like IEC 61340.
4. Mobility with stability
Technicians tend to roll around when doing complex assembly or inspection work. Chairs must offer:
- Smooth-rolling castors for harsh industrial floors
- Brake-loaded wheels for preventing roll-around movement when seated
- Swivel action for multitasking or instrument switching
Mobility should not, however, compromise stability. A wide five-leg base and low center of gravity reduce tipping hazard, which is an especial concern in active work environments.
5. Cleanability and Compliance
Singapore’s aerospace sector has a tendency to adopt stringent quality management processes like AS9100 and is subject to audit and compliance checks. Chairs must be easy to clean and possess a hygienic appearance—especially in areas where FOD (Foreign Object Debris) control is exercised.
Perfect materials are:
- PU foam or integral skin: tear-proof and wipe-clean
- Sealed joints: to prevent particle build-up
- Low usage of fabric: to avoid lint and dust buildup
Cleanliness and conformance of seating serve not only safety but also aid in sustaining visual workplace standards like 5S.
Bonus Consideration: Task-Specific Design
In some aerospace factories, seating needs are radically different from department to department. Below are some custom scenarios:
- Inspection labs: Require foot rings and height-adjustable stools for use with microscopes.
- Paint shops: Need chairs with low joints and solvent-resistant materials.
- Production floors: Choose durable, ergonomic task chairs with anti-fatigue support.
Selecting task-based seating ensures every team gets the support they need when it comes to their everyday movement and posture.
How the Right Chair Impacts Your Aerospace Team
Don’t forget the ripple effects of great seating:
| Impact Area | Benefit of the Right Industrial Chair |
| Worker Comfort | Reduces fatigue and risk of injury |
| Productivity | Maintains focus and continuity in high-precision work |
| Quality Control | Minimizes mistakes in crucial assembly |
| EHS Compliance | Makes it easier to comply with ergonomic and safety audits |
| Cost Efficiency | Saves long-term replacement and downtime costs |
Conclusion
In Singapore’s competitive aerospace market, it’s not about the aircraft—it’s about the people and the equipment they use on a daily basis. A well-designed industrial chair is more than office furniture; it’s a productivity companion and a safety feature rolled into one.
By making ergonomic adjustability, ESD protection, durability, and cleanability top priorities, aerospace businesses can design safer, more productive working environments that are responsive to both technical requirements and human needs.